Building on Ollie’s previous blog, in which he built a TCP proxying service into a Thinkst Canary device with their module capability, I took a look at practical use case for this functionality and how it can be used to make the facade of a Canary have more interactivity.
What a Canary is
A Canary is excellent at providing a low noise digital tripwire, which is a powerful tool to detect Red Teamers or malicious threat actors attempting to move laterally in an environment. It does this in part by presenting dummy services, something that is not real but a python script behaving as the application would whilst being present.
Let’s take a look at the SSH module that comes with OpenCanary. In this example we can see the Twisted framework used to present responses that an SSH service would, such as building in ways of handling bad packets or lost of connections (see the sendDisconnect and connectionLost functions) meaning that if profiled it looks consistent with an actual OpenSSH server:
This module will never return a shell, instead returning an invalid credentials message every time using the error function twisted.cred library:
We wanted more
We wanted a way to collect more information and intelligence about a potential intruder. We wanted to present them with an actual shell so that we can monitor and further understand any subsequent activity. Whilst it is possible to create a dummy terminal in Python, it doesn’t seem wise as there are so many combinations of commands, files and techniques that an attacker might use that we would have to account for. In addition, if the terminal is limited, it may alert the attacker quickly to the end device being a trap.
Using Ollie’s TCP Relay module, we can maintain the benefits of having a locally installed Canary that behaves and appears as a device that belongs in the environment (i.e. it is configured with a profile to be a representative device for the organisation) but then also presents a contextualised shell when asked. Utilising a technology like Docker means that we can create individually maintained container that can represent that organisation.
As we also know the breakout points of the Canary devices we can we can use Network Address Translation (NAT) to route it to the correct container dynamically.
Below is a diagram that shows the set-up:
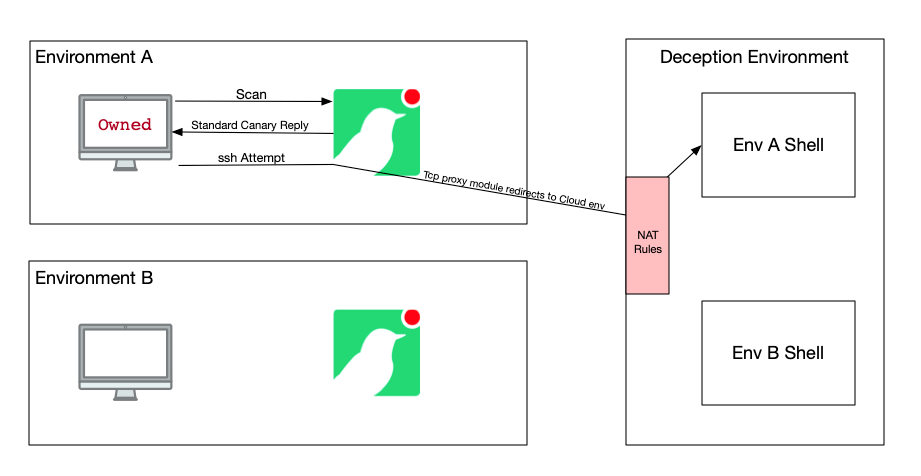
The build
In order to build the environment in figure 1, I started by researching how to best make a docker container that would allow me to host a shell. Luckily for me Docker themselves had already provided documentation and an example build file to do that. Here’s the code I ended up using:
FROM ubuntu:16.04
RUN apt-get update apt-get install -y openssh-server
RUN mkdir /var/run/sshd
RUN echo 'root:toor' | chpasswd
RUN sed -i 's/PermitRootLogin prohibit-password/PermitRootLogin yes/' /etc/ssh/sshd_config
# SSH login fix. Otherwise user is kicked off after login
RUN sed 's@sessions*requireds*pam_loginuid.so@session optional pam_loginuid.so@g' -i /etc/pam.d/sshd
ENV NOTVISIBLE "in users profile"
RUN echo "export VISIBLE=now" >> /etc/profile
EXPOSE 22
CMD ["/usr/sbin/sshd", "-D"]Here we can see the commands needed to prevent the SSH service from dying on connect and that it exposes TCP port 22 from the container. It is important to note that this port is for the container and not the host system, we’ll specify the host port when we run the container.
In addition, there are a few items to edit here; we could change the root password for example. Or we could create a user in the build file and with some trusted keys and a password deployed, which we could then sprinkle the associated private key around our environment.
In order to make them specific to each customer, we’ll keep a Dockerfile per environment to manage the containers easily.
Next up was to create some Ansible code to prepare and run these containers on a host. In this example I built a host in AWS so that it would be easier to make publicly available on the relevant ports.
The Ansible code was written to:
- Install software dependencies for Docker to run
- Install the latest version of Docker
- Create the directories for the Dockerfiles and other config to exist and copy them over
- Build and run the containers on the box, exposing a specific port and give them a “normal” hostname
- Create a NAT for certain source IPs to route them to the correct exposed port
Here’s the rough Ansible code that I wrote to take care of this:
In this example code I created two “environments”, one named LiamTest and another called NCCGroup.
Testing the solution
Now we need to test the solution, to make sure that the Canary behaves as we expect (as a fake Ubuntu server) and routes the SSH session to the correct external Docker container.
First, here’s the results of an nmap scan which shows the Canary behaving like a regular device:
liam@LiamTestEnv ~ % sudo nmap -sV 192.168.0.29
Starting Nmap 7.80 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2020-09-11 16:12 BST
Nmap scan report for 192.168.0.29
Host is up (0.00075s latency).
Not shown: 996 closed ports
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
21/tcp open ftp vsftpd 2.3.5
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 7.2p2 Ubuntu 4ubuntu2.10 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0)
80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.2.22 ((Ubuntu))
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D5:AD:2C (Oracle VirtualBox virtual NIC)
Service Info: OSs: Unix, Linux, IOS; Device: router; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel, cpe:/o:cisco:ios
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 34.31 secondsNext here is a SSH login from the Canary deployed in the “LiamTest” environment:
liam@LiamTestEnv ~ % ssh root@192.168.0.29
The authenticity of host '192.168.0.29 (192.168.0.29)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:Z4rpxjNSUZlph6IKiyo8SkzFS+2JgqXPXa79kTalARI.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no/[fingerprint])? yes
Warning: Permanently added '192.168.0.29' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
root@192.168.0.29's password:
Welcome to Ubuntu 16.04.7 LTS (GNU/Linux 5.3.0-1035-aws x86_64)
* Documentation: https://help.ubuntu.com
* Management: https://landscape.canonical.com
* Support: https://ubuntu.com/advantage
Last login: Fri Sep 11 14:27:21 2020 from 172.17.0.1
root@LAP4321:~# hostname
LAP4321And finally, a test logging into the NCC Group environment:
liam@NCCGroupEnv ~ % ssh root@10.43.5.23
The authenticity of host '10.43.5.23 (10.43.5.23)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:nKocXZ7YRsLBx5NMa7LZsqr5qgm1XKX4O9QpijzKhbQ.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no/[fingerprint])? yes
Warning: Permanently added '10.43.5.23' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
root@10.43.5.23's password:
Welcome to Ubuntu 16.04.7 LTS (GNU/Linux 5.3.0-1035-aws x86_64)
* Documentation: https://help.ubuntu.com
* Management: https://landscape.canonical.com
* Support: https://ubuntu.com/advantage
Last login: Fri Sep 11 14:28:42 2020 from 172.17.0.1
root@SRV1234:~# hostname
SRV1234More to do
In order to make the extension more effective there are few other things that still need doing:
- Instrumentation to monitor what is happening the container
- Deployment of credentials/SSH keys around the network to lead attackers here
- Add more custom environment artifacts to the container
- Emulate other services that are close to the environments configuration
- Build a small network that is accessible by the docker containers to encourage lateral movement attempts
Why?
NCC Group’s Managed Network Intruder Alarm service as part of our Managed Detection and Response offering uses Canaries. We can see the potential for gaining better intelligence on adversaries to shorten the containment and response phases through extending their functionality.
